Category: Printer
Manufacturer: Fargo
Caution Level: Safe
Download File Size: 6.68 MB
Operating System: Windows XP, Windows 2000, Windows ME, Windows 98
Latest Version / Release Date: 2.1.3 / 07 Oct 2005
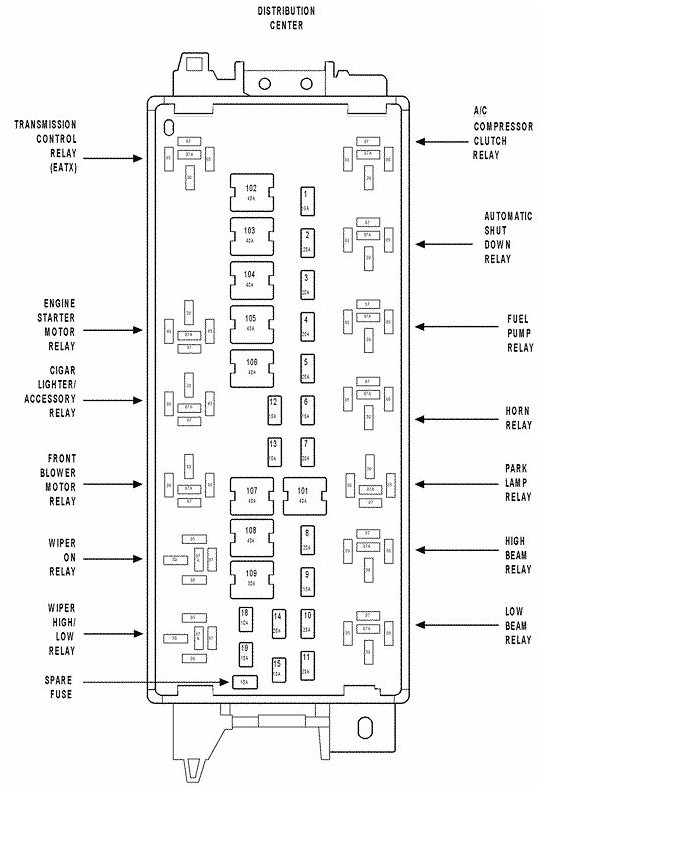
Before starting the installation of drivers, connect your printer Fargo DTC 550 to your computer, and that the printer is powered On. See your printer manual for details. Drivers with status monitoring can report printer and print job status to the Windows Spooler and other Windows applications, including BarTender. Downloaded fonts typically print faster, because they can be rendered directly by the printer. Otherwise they have to first be rasterized by Windows and output to the printer as bitmaps. The Delaware Transit Corporation is an equal opportunity employer and service provider. We consider applicants for all positions without regard to race, color, religion, sex/gender identity, national origin, marital or veteran status, age, disability, pregnancy, political opinion or affiliation.
Windows device driver information for DTC300 Card Printer
The DTC300 Card Printer device is developed to make securing users’ organizations and issuing ID (identification) cards easier and a lot simpler. This device is very easy to utilize, reliable, and there’s virtually no maintenance or learning curve. This printer device also allows users to increase their productivity via incorporating their new identification cards with their current attendance and time, access control or visitor management systems. The DTC300 Card Printer device boasts of convenient and exclusive functions that make it one of the best and easiest to utilize printer devices in its class. This device is an entry level printer perfect for low to medium security applications. It is targeted to organizations that require minimal maintenance and intuitive operations. This printer device features easy loading by providing the innovative SmartLoad Ribbon Cartidge along with the SmartClean Roller.
Outdated Drivers?
Dtc1000 Drivers
Unless you update your drivers regularly you may face hardware performance issues.
To check your drivers you should manually verify every device on your system for driver updates
This printer device also comes with the easy to use SmartScreen LCD (liquid crystal display) Control Panel that allows users to keep track of the status of the printer device. It also has added capabilities such as an encoding module for mag stripe, e-card and proximity. The DTC300 printer device is likewise capable of implementing 2 sided printing operations with an additional optional module. It also comes bundled with the software application called the Free Card Identity. The SmartLoad Ribbon Cartridge that comes with this printer device is capable of saving time and aiding in getting rid of the extra expense of torn ribbons. This device is used by K-12 Schools, small to mid sized businesses, local an state governments, parks and recreation, health clubs, recreational facilities, ski lodges and resorts, memberships, retail, as well as customer loyalty. The DTC300 printer device is manufactured and marketed by Fargo. It is highly recommended you run a free registry scan for Windows and DTC300 Card Printer errors before installing any driver updates.
What are DTCs or diagnostic trouble codes? What does a DTC mean in a vehicle, and how does it work?
These are questions that some commercial drivers, fleet managers, and safety officers may have.
What does a DTC mean?
If a vehicle has a problem, the on-board diagnostics system usually detects the issue and generates the appropriate code that you can use to identify the issue. These codes are commonly known as DTC or diagnostic trouble codes.
DTCs are how the J-1939 (in heavy-duty vehicles) and OBD-II (light-duty vehicles) indicate the on-board problems.
Each code indicates a specific fault in the vehicle. DTCs help you understand what the problem is, solve that problem quickly, and get back on the road without wasting a lot of time.
DTCs were created by the SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers), which is now known as SAE International and develops standards for automotive engineers.
Now, let’s see how a typical OBD-II code is displayed, what it means, and how to interpret it.
Format of the OBD-II diagnostic trouble code
A diagnostic trouble code is generally divided into four sections: one letter and four numbers. It usually has five characters.
Let’s use the following code as an example: P0430.
Here are the four sections a DTC is divided into and their detailed explanation.
1. System or category
The first letter in the code, which in this case is P, represents the system or category of the DTC. It pinpoints the related system.
The OBD-II diagnostic trouble codes are categorized into four different systems or categories:
- B-codes refer to the body. This category covers parts that are mainly found in the passenger compartment area and is mainly concerned with driver-related functions, such as safety and convenience.
- C-codes refer to the chassis category, which deals with areas outside the passenger compartment. It covers functionalities, such as brakes, suspension, steering, and mechanical systems.
- P-codes refer to the powertrain category. This category covers functions that include transmission, engine, and associated drivetrain accessories.
- U-codes refer to network and vehicle integration and cover functions managed by the on-board computer system.
As in our example (P0430), the DTC code starts with P, we know that the vehicle issue is related to the powertrain system.
2. Generic and manufacturer specific codes
The second number in the DTC represents either a generic or manufacturer specific code. Generally, you will see DTCs starting with either a 0 or 1.
DTCs that start with 0 as the first digit after the letter that represents the system refer to generic codes. In other words, 0 refers to generic faults. It represents a generic code that is followed by all OBD-II vehicles.
On the other hand, codes starting with 1 are manufacturer specific codes. These codes are unique to the specific model of the vehicle.
In our example of P0430, the first number is 0, which means it is a generic code.
3. Subsystems
The third character (number) in the diagnostic trouble code indicates the subsystem in which the fault is.
The powertrain category (P) has eight subsystems:
- 0 – Fuel and air metering and auxiliary emission controls
- 1 – Fuel and air metering
- 2 – Fuel and air metering – injector circuit
- 3 – Ignition systems
- 4 – Auxiliary emission controls
- 5 – Vehicle speed control and engine idling
- 6 – Computer and auxiliary outputs
- 7 – Transmission
Sometimes, you may also see a letter (A, B, or C) instead of a number in the DTC. In that case, these three letters refer to the hybrid propulsion systems.
In our example, the third character (P0430) represents an issue with auxiliary emission controls.
4. Fault code description
The last two numbers (sometimes, three) in the DTC refer to the actual fault description. It can be any number between 0 to 99.
In our example (P0430), it is 30, which indicates that the catalyst system efficiency is below the threshold. There could be multiple reasons for that, e.g., a faulty catalytic converter, engine mechanical damage, exhaust leak, or a leaking fuel injector.
You can check the complete list of OBD-II fault code descriptions here.
Here is a graphical representation of diagnostic trouble codes are interpreted.
How KeepTruckin helps with fault code detection and vehicle maintenance
DTCs or diagnostic trouble codes can help pinpoint the exact issue in a vehicle. Vehicle downtime is a problem that companies may struggle with. Downtime hampers their customer service, productivity, and profitability.
If you have the KeepTruckin fleet management solution installed, these DTC codes can be redirected to safety and dispatchers. These managers can then take immediate action to keep disruptions to a minimum.
The KeepTruckin Vehicle Gateway automatically monitors fault codes and can send instant, real-time alerts to the KeepTruckin Dashboard and fleet managers with actionable descriptions if an issue occurs.
Recurring issues are also highlighted, so you can identify important issues faster.
Drivers can also report a defect while creating vehicle inspection reports with the KeepTruckin App, which also sends an alert in the KeepTruckin Dashboard.
Furthermore, you can also view the fault code detail reports for any vehicle or group for a specific time period to anticipate when maintenance will be required. These reports can also be exported and downloaded in your preferred format (CSV or PDF).
Timely identification of DTCs may increase efficiency and save money
Dtc4000 Drivers
By timely identifying vehicle-related issues with the KeepTruckin fleet management solution, you may avoid costly repairs, minimize vehicle downtime, provide better service to your customers, and increase profitability.
Dtc Drivers
As more data is gathered, you can also look into historical reports, identify recurring issues, and stay on top of your vehicle health for smooth operations across the entire fleet.
Learn more about DTC codes in our guide.
Disclaimer: All content and information on this website is for informational and educational purposes only, does not constitute financial, business, or legal advice. Although KeepTruckin strives to provide accurate general information, the information presented here is not a substitute for any kind of professional advice, and you should not rely solely on this information. Always consult a professional in the area for your particular needs and circumstances prior to making any professional, legal, business, and financial or tax-related decisions.
Some of the links contained within this site will let you leave the KeepTruckin website. The linked sites are not under the control of KeepTruckin, nor is KeepTruckin responsible for the contents of any linked site or any link contained in a linked site. These links are provided to you only as a convenience, and the inclusion of any link does not imply endorsement of the site or affiliation.

